Page 79 - Sugam Sarita
P. 79
urban sectors and is the main source of drinking water for most of the
towns along its course. More than 70% of the drinking water supply of
Delhi is abstracted from the river Yamuna (CPCB, 1996., Upadhyay
et al., 2010). An estimated 57 million people are dependent on the
water of the Yamuna River.
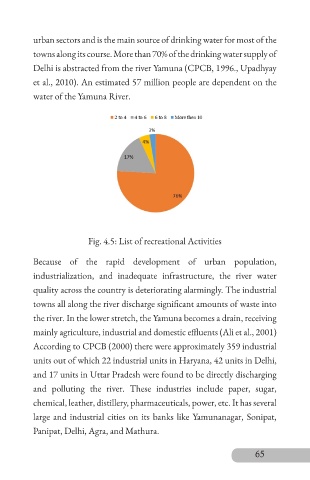
Fig. 4.5: List of recreational Activities
Because of the rapid development of urban population,
industrialization, and inadequate infrastructure, the river water
quality across the country is deteriorating alarmingly. The industrial
towns all along the river discharge significant amounts of waste into
the river. In the lower stretch, the Yamuna becomes a drain, receiving
mainly agriculture, industrial and domestic effluents (Ali et al., 2001)
According to CPCB (2000) there were approximately 359 industrial
units out of which 22 industrial units in Haryana, 42 units in Delhi,
and 17 units in Uttar Pradesh were found to be directly discharging
and polluting the river. These industries include paper, sugar,
chemical, leather, distillery, pharmaceuticals, power, etc. It has several
large and industrial cities on its banks like Yamunanagar, Sonipat,
Panipat, Delhi, Agra, and Mathura.
65