Page 165 - Abhivruddhi
P. 165
with civil wars in Sri Lanka. A background paper for World Bank written
by Strand H. et al. (2010) analyses the economic consequences of war
for the past decade in the MENA (the Middle East and North Africa)
region. Fukuda-Parr S. et al. (2012) in their work, review the relationship
between armed conflicts and development in sub-Saharan Africa. It
sates war is development in reverse and studies the effect on poverty and
development, highlighting horizontal inequalities created, casualties and
human costs.
Research methods:
The data included in the present article is secondary and is acquired
from the available reports. Majority of the data is taken from the two
reports published by the Institute of Economics and Peace (IEP); Economic
Value of Peace published in 2018 and Global Peace Index, published in
2019. The Institute for Economics and Peace is a non-partisan, non-profit
think-tank that works towards development in peace and human welfare.
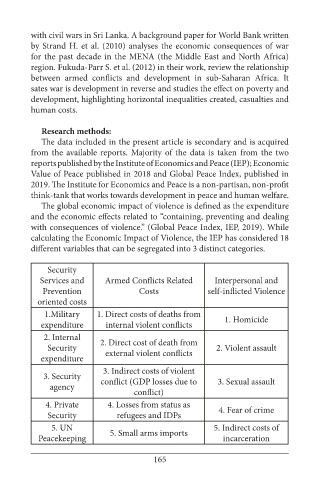
The global economic impact of violence is defined as the expenditure
and the economic effects related to “containing, preventing and dealing
with consequences of violence.” (Global Peace Index, IEP, 2019). While
calculating the Economic Impact of Violence, the IEP has considered 18
different variables that can be segregated into 3 distinct categories.
Security
Services and Armed Conflicts Related Interpersonal and
Prevention Costs self-inflicted Violence
oriented costs
1.Military 1. Direct costs of deaths from
expenditure internal violent conflicts 1. Homicide
2. Internal 2. Direct cost of death from
Security 2. Violent assault
expenditure external violent conflicts
3. Indirect costs of violent
3. Security conflict (GDP losses due to 3. Sexual assault
agency
conflict)
4. Private 4. Losses from status as 4. Fear of crime
Security refugees and IDPs
5. UN 5. Indirect costs of
Peacekeeping 5. Small arms imports incarceration
165